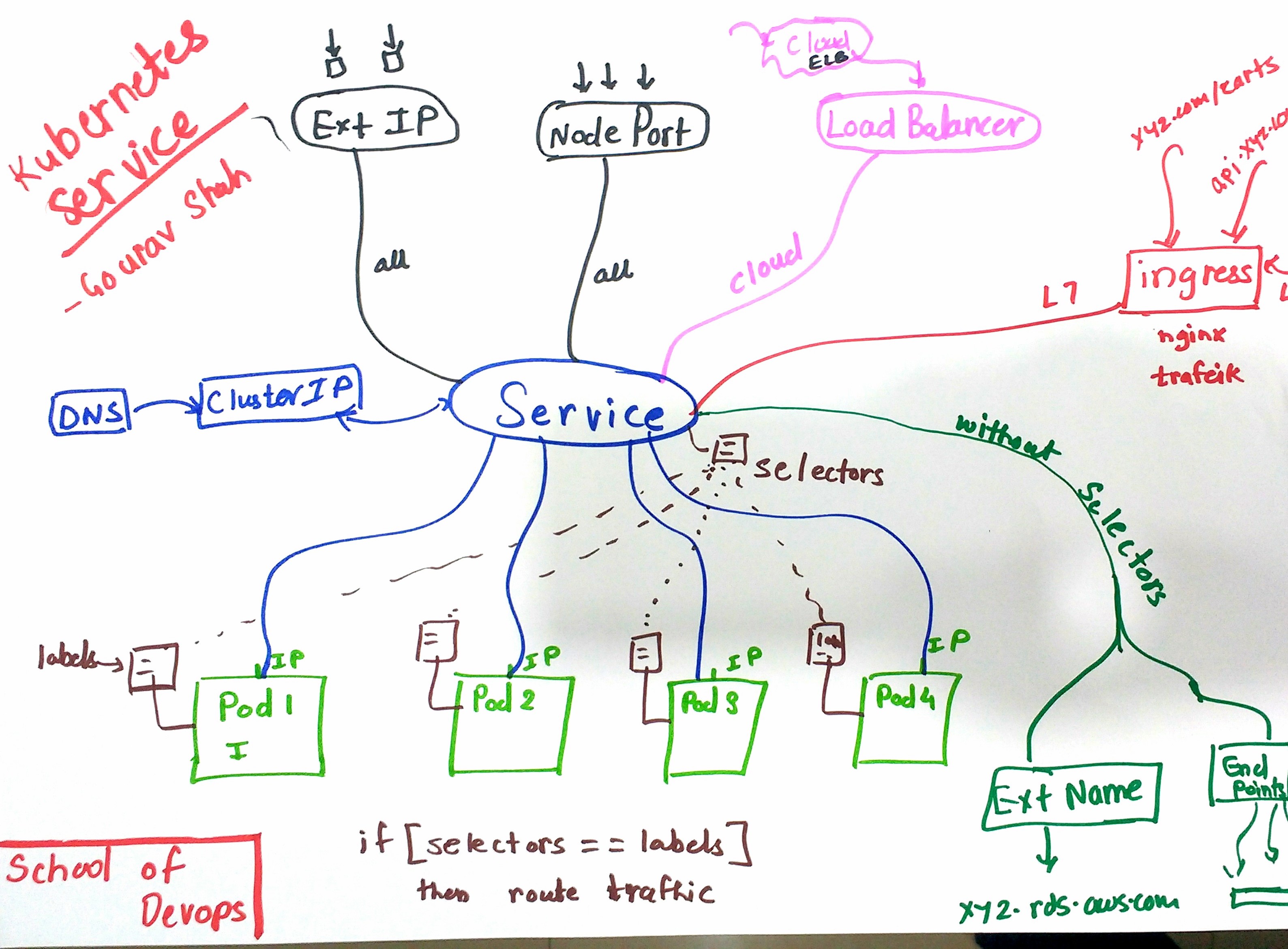
Exposing Application with a Service
Types of Services:
- ClusterIP
- NodePort
- LoadBalancer
- ExternalName
kubectl get pods
kubectl get svc
Sample Output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
voting-appp-1j52x 1/1 Running 0 12m
voting-appp-pr2xz 1/1 Running 0 9m
voting-appp-qpxbm 1/1 Running 0 15m
Setting up monitoring
If you are not running a monitoring screen, start it in a new terminal with the following command.
watch -n 1 kubectl get pod,deploy,rs,svc
Writing Service Spec
Lets start writing the meta information for service.
Filename: vote-svc.yaml
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: vote
labels:
role: vote
spec:
And then add the spec to it. Refer to Service (v1 core) api at this page https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/generated/kubernetes-api/v1.10/
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: vote
labels:
role: vote
spec:
selector:
role: vote
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
nodePort: 30000
type: NodePort
Save the file.
Now to create a service:
kubectl apply -f vote-svc.yaml --dry-run
kubectl apply -f vote-svc.yaml
kubectl get svc
Now to check which port the pod is connected
kubectl describe service vote
Check for the Nodeport here
Sample Output
Name: vote
Namespace: instavote
Labels: role=svc
tier=front
Annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration={"apiVersion":"v1","kind":"Service","metadata":{"annotations":{},"labels":{"role":"svc","tier":"front"},"name":"vote","namespace":"instavote"},"spec":{...
Selector: app=vote
Type: NodePort
IP: 10.108.108.157
Port: <unset> 80/TCP
TargetPort: 80/TCP
NodePort: <unset> 31429/TCP
Endpoints: 10.38.0.4:80,10.38.0.5:80,10.38.0.6:80 + 2 more...
Session Affinity: None
External Traffic Policy: Cluster
Events: <none>
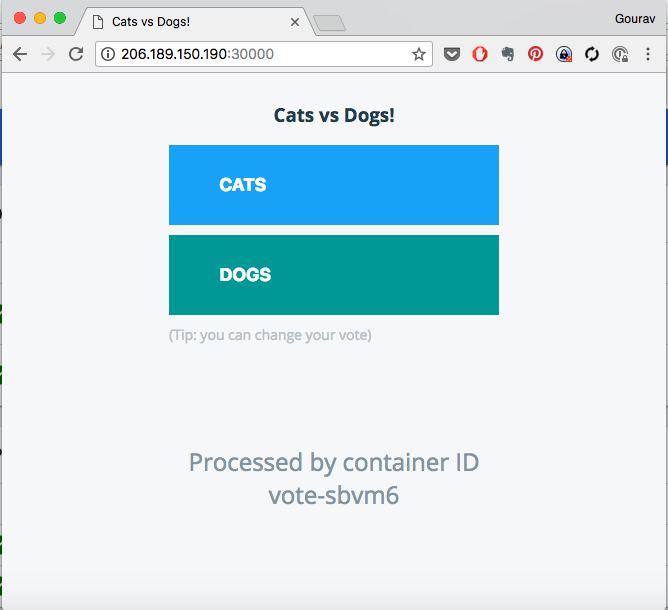
Go to browser and check hostip:NodePort
Here the node port is 31429.
Sample output will be:
Exposing the app with ExternalIP
spec:
selector:
role: vote
ports:
- port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 80
type: NodePort
externalIPs:
- xx.xx.xx.xx
- yy.yy.yy.yy
Where
replace xx.xx.xx.xx and yy.yy.yy.yy with IP addresses of the nodes on two of the kubernetes hosts.
apply
kubectl get svc
kubectl apply -f vote-svc.yaml
kubectl get svc
kubectl describe svc vote
[sample output]
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
vote NodePort 10.107.71.204 206.189.150.190,159.65.8.227 80:30000/TCP 11m
where,
EXTERNAL-IP column shows which IPs the application is been exposed on. You could go to http://
Internal Service Discovery
- Visit the vote app from browser
- Attemp to vote by clicking on one of the options
observe what happens. Does it go through?
Debugging,
kubectl get pod
kubectl exec vote-xxxx ping redis
[replace xxxx with the actual pod id of one of the vote pods ]
keep the above command on a watch. You should create a new terminal to run the watch command.
e.g.
watch kubectl exec vote-kvc7j ping redis
where, vote-kvc7j is one of the vote pods that I am running. Replace this with the actual pod id.
Now create redis service
kubectl apply -f redis-svc.yaml
kubectl get svc
kubectl describe svc redis
Watch the ping and observe if its able to resolve redis by hostname and its pointing to an IP address.
e.g.
PING redis (10.102.77.6): 56 data bytes
where 10.102.77.6 is the ClusterIP assigned to the service.
What happened here?
- Service redis was created with a ClusterIP e.g. 10.102.77.6
- A DNS entry was created for this service. The fqdn of the service is redis.instavote.svc.cluster.local and it takes the form of my-svc.my-namespace.svc.cluster.local
- Each pod points to internal DNS server running in the cluster. You could see the details of this by running the following commands
kubectl exec vote-xxxx cat /etc/resolv.conf
[replace vote-xxxx with actual pod id]
[sample output]
nameserver 10.96.0.10
search instavote.svc.cluster.local svc.cluster.local cluster.local
options ndots:5
where 10.96.0.10 is the ClusterIP assigned to the DNS service. You could co relate that with,
kubectl get svc -n kube-system
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kube-dns ClusterIP 10.96.0.10 <none> 53/UDP,53/TCP 1h
kubernetes-dashboard NodePort 10.104.42.73 <none> 80:31000/TCP 23m
where, 10.96.0.10 is the ClusterIP assigned to kube-dns and matches the configuration in /etc/resolv.conf above.
Creating Endpoints for Redis
Service is been created, but you still need to launch the actual pods running redis application.
Create the endpoints now,
kubectl apply -f redis-deploy.yaml
kubectl describe svc redis
[sample output]
Name: redis
Namespace: instavote
Labels: role=redis
tier=back
Annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration={"apiVersion":"v1","kind":"Service","metadata":{"annotations":{},"labels":{"role":"redis","tier":"back"},"name":"redis","namespace":"instavote"},"spec"...
Selector: app=redis
Type: ClusterIP
IP: 10.102.77.6
Port: <unset> 6379/TCP
TargetPort: 6379/TCP
Endpoints: 10.32.0.6:6379,10.46.0.6:6379
Session Affinity: None
Events: <none>
Again, visit the vote app from browser, attempt to register your vote and observe what happens now.
Reading
Debugging
* Services
* Kubernetes Services Documentation
* Service API Specs for Kubernetes Version 1.10